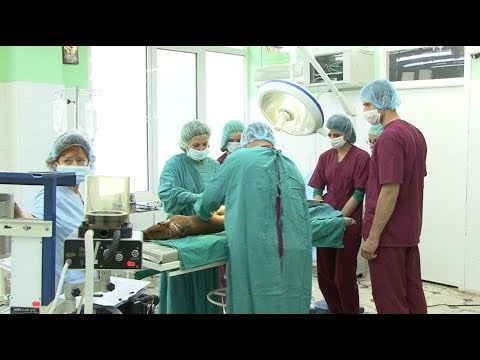
All Bulgarian Medical Universities offer postgraduate medical study programs (specialisation training or residency specialisation) for graduates who have completed their 6-year undergraduate medical studies that have led to a Master’s Degree.
What are the Benefits of Postgraduate Training for Medicine Students in Bulgaria
Subsequently, after graduation, students must specialise in a medical field which typically lasts 4-6 years depending on the programme they have graduated from. Postgraduate medical study focuses on the acquisition of a medical speciality according to the approved EU training medical programmes, and is complete once students have finished licensure examinations offered by the State Examination Commission if specialisation takes place in Bulgaria. Most medical graduates of Bulgarian medical universities, whether Bulgarian, EU citizens or non-EU citizens, prefer to continue with their specialisation in Bulgaria.
What Languages are the Postgraduate Medical Study Programmes in Bulgaria Taught in
Note that it is imperative by this time that all foreigners (EU and non EU candidates) should have at least some competency in the Bulgarian language or take a 9-month preparatory course culminating with a Bulgarian language exam (B2 level in the EU framework) usually at the University, so as to be able to communicate with patients they treat in hospitals, as is the case in any country that a medical professional seeks specialisation.
What Student Preparations are Needed for Postgraduate Residency Study and Specialisation in Bulgaria
Bulgarian medical specialisation training takes place at the Medical University Hospitals or affiliated clinics and it includes full-time practical training 8 hours per day in a position with duties pertaining to the curricula of respective specialities. In every medical University there is a Commission for Postgraduate Education appointed by the Rector, and admits to the Speciality State Examination only the candidates who have completed the respective specialisation curricula successfully. In turn, medical specialists who have successfully passed the Speciality State Examination receive a certificate of a recognised speciality by the Medical University.
What is the Process for Medical Residency Specialisation Positions including Examinations in Bulgaria
Every year, medical residency specialisation positions are announced on the website of the Ministry of Healthcare (www.mh.government.bg) by the end of October, in the section “Normative Acts” under the heading “Regulations, Instructions and Orders”, and are separate for EU candidates (including Bulgarians) and non-EU candidates, based on availability of funding, not the experience gained. In turn, EU candidates including Bulgarians are admitted to specialisation positions through an application as well as a mandatory residency examination process and subsequently must secure funding, but non-EU candidates are admitted through an application process as they are self-funded.
In order for a specialisation position to be secured, be it through government funding, sponsoring or self-funded, besides the relevant documentation that is required when applying for specialisation, all EU applicants including Bulgarians must complete an entrance or eligibility exam. This Specialty State entrance Examination lasts 4 hours, during which candidates must expand on 2 topics from a given list of topics.
Can Students Fund their Postgraduate Specialisation Position in Bulgaria
More specifically, with regard to funding for such specialisation positions, both non-EU students and EU students may choose to pay for their specialisation themselves, so long as they have found a position, adducing a specialisation fee to the University of about £3,650 in two instalments, annually.
Alternatively, for EU candidates only (including Bulgarians), funding is available for specialisation positions announced by the Ministry of Healthcare (leading to respective residency Specialty State Examinations) in any of the following three ways:
- The Bulgarian Government pays the Medical University specialisation fees of each Postgraduate Medical student trained (monthly: 180 BGN, for every Medical student or 600 BGN, for every Dental student) as well as the monthly salary of the Postgraduate Medical or Dental student (600–900).
- A sponsor pays the monthly specialisation fees to the Medical University (180 BGN, if Medical student or 600 BGN, if Dental student) and the monthly salary of the Medical or Dental student (600–900).
- The Postgraduate students themselves pay the specialisation fees to the Medical University 180 BGN, if Medical student or 600 BGN, if Dental student) and he or she might get a monthly salary of up to 600 BGN, if any funds are available through EU grants.
As should be expected, competition for Bulgarian Government funding of specialisation positions is very high, but it is considerably lower when it comes to Sponsorships, or if sought specialisation training positions are self-funded.
Securing Medicine Specialisation Positions & Funding (if EU-candidates, including Bulgarians)
By January, about three months after the Ministry has publicised the available positions for postgraduate specialisation, each Medical University will announce and advertise in local daily newspapers and on the official University website the commencement of a competition for all three aforementioned ways of funding pertaining to such specialisation programmes.
After the University’s announcement, candidates have one month to apply, by submitting relevant documentation to the Medical University for assessment, as well as prepare for Specialty State entrance Examination if applying for government funding. Subsequently, ranking of successful candidates as well as the position that each candidate secured and whether admission is sponsored, supported by government funding or self-funded, is publicised by the University.
If any positions are not covered, then Medical Universities will announce once more the available positions sometime between July and August, giving applicants 3 month to submit applications. This cycle repeats throughout the year.
Below are listed the necessary documents to complete the process which must be certified, notarised and translated if necessary:
- Application Form for the specialty they wish to acquire;
- Curriculum Vitae;
- Notarised Copy of Degree of completed medical education;
- Medical Certificate issued within one month prior to the date of application;
- Certificate of competency or proficiency in Bulgarian and credentials that prove possession of knowledge in professional terminology in Bulgarian (All Foreign Students);
- Certificate of recognition of the Medical Degree acquired after 6 years of study in another country apart from Bulgaria (Foreign students).
The Medical and Dental Specialisations for Study in Bulgaria are:
| No | Specialty | Years | |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. Specialities included in EU Directive 2005/36/EC on the Recognition of Professional Qualifications | |||
| I. Specialities for holders of Master degree in Medicine | |||
| Ia. Specialties with predominant therapeutic focus | |||
| 1. | Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care | 4 | |
| 2. | Internal Medicine | 5 | |
| 3. | Gastroenterology | 4 | |
| 4. | Geriatric Medicine | 4 | |
| 5. | Child Psychiatry | 4 | |
| 6. | Paediatrics | 4 | |
| 7. | Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases | 4 | |
| 8. | Infectious Diseases | 4 | |
| 9. | Cardiology | 4 | |
| 10. | Clinical Allergy | 4 | |
| 11. | Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics | 4 | |
| 12. | Clinical Haematology | 4 | |
| 13. | Skin and Venereal Diseases | 4 | |
| 14. | Radiotherapy | 4 | |
| 15. | Nerve Diseases | 4 | |
| 16. | Nephrology | 4 | |
| 17. | General Medicine | 3 | |
| 18. | Pneumology and phthisiatrics | 4 | |
| 19. | Psychiatry | 4 | |
| 20. | Rheumatology | 4 | |
| 21. | Emergency Medicine | 5 | |
| 22. | Haematology and Blood Transfusion | 4 | |
| 23. | Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation | 4 | |
| 23a. | Medical Oncology | 5 | |
| Ib. Specialities with predominant focus | |||
| 24. | Obstetrics and Gynaecology | 4 | |
| 25. | Thoracic Surgery | 5 | |
| 26. | Paediatric Surgery | 5 | |
| 27. | Cardiac Surgery | 5 | |
| 28. | Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery | 5 | |
| 29. | Neurosurgery | 5 | |
| 30. | Orthopaedics and Traumatology | 5 | |
| 31. | Ophthalmology | 4 | |
| 32. | Plastic Reconstructive and Aesthetic Surgery | 5 | |
| 33. | Vascular Surgery | 5 | |
| 34. | Urology | 5 | |
| 35. | Ear, Nose and Throat Diseases | 4 | |
| 36. | Surgery | 5 | |
| Ic. Specialities with prevalent clinical-diagnostic focus | |||
| 37. | Biochemistry | 4 | |
| 38. | Clinical Immunology | 4 | |
| 39. | Clinical Laboratory | 4 | |
| 40. | Microbiology | 4 | |
| 41. | Nuclear Medicine | 4 | |
| 42. | Image Diagnostics | 4 | |
| 42a. | General and Clinical Pathology | 4 | |
| 42b. | Radiobiology | 4 | |
| 42c. | Medical Genetics | 4 | |
| Id. Specialties with another focus | |||
| 43. | Communal Hygiene | 4 | |
| 44. | Social Medicine and Health Management | 4 | |
| 45. | Occupational Medicine | 4 | |
| 46. | Pharmacology | 4 | |
| II. Specialities for holders of Master degree in Dental Medicine | |||
| 1. | Oral Surgery | 3 | |
| 2. | Orthodontics | 3 | |
| III. Specialties for holders of Master degree in Medicine or Master degree in Dental Medicine | |||
| 1. | Dental, Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery | 4 | |
| B. Specialities which are not included in EU Directive 2005/36/EC on the Recognition of Professional Qualifications | |||
| I. Specialities for holders of Master degree in Medicine | |||
| Ia. Specialties with predominant therapeutic focus | |||
| 1. | Angiology | 4 | |
| 2. | Paediatric Gastroenterology | 4 | |
| 3. | Paediatric Endocrinology and Metabolic Diseases | 4 | |
| 4. | Paediatric Cardiology | 4 | |
| 5. | Paediatric Clinical Haematology and Oncology | 4 | |
| 6. | Paediatric Neurology | 4 | |
| 7. | Paediatric Nephrology and Haemodialysis | 4 | |
| 8. | Paediatric Pneumology and Phthisiatrics | 4 | |
| 9. | Paediatric Rheumatology | 4 | |
| 10. | Clinical Toxicology | 4 | |
| 11. | Medical Parasitology | 3 | |
| 12. | Neonatology | 4 | |
| 13. | Sports Medicine | 4 | |
| 14 | Forensic Psychiatry | 4 | |
| 14a. | Occupational Diseases | 4 | |
| Ib. Specialities with prevalent clinical-diagnostic focus | |||
| 15. | Aviation Medicine | 3 | |
| 16. | Virology | 3 | |
| 17. | Epidemiology of Infectious Diseases | 3 | |
| 18 | Pathophysiology | 3 | |
| 19. | Forensic Medicine | 3 | |
| 20. | Toxicology | 3 | |
| Ic. Specialities with another focus | |||
| 21. | Healthcare Economics | 2 | |
| 22. | Medicine of Disasters (Catastrophes) | 3 | |
| 23. | General Hygiene | 3 | |
| 24. | Radiation Hygiene | 3 | |
| 25. | Hygiene of Childhood and Adolescence | 3 | |
| 26. | Nutrition and Dietetics | 3 | |
| II. Specialities for persons with Master degree in Dental Medicine | |||
| 1. | Paediatric Dental Medicine | 3 | |
| 2. | General Dental Medicine | 3 | |
| 3. | Operative Dentistry and Endodontics | 3 | |
| 4. | Periodontics and Oral Mucosal Diseases | 3 | |
| 5. | Prosthetic Dental Medicine | 3 | |
| 6. | Social Medicine and Public Dental Health | 3 | |
| 7. | Dental Clinical Allergy | 3 | |
| III. Specialties for holders of Master degree in Medicine – lecturers at Faculties of Dental Medicine or Master degree in Dental Medicine | |||
| 1. | Dental Image Diagnostics | 3 | |
| IV. Specialties for holders of Master degree in Pharmacy | |||
| 1. | Analysis of Medicinal Products | 3 | |
| 2. | Clinical Pharmacy | 3 | |
| 3. | Medicinal Plants and Phytopharmaceutical Products | 3 | |
| 4. | Organisation and Economics of Distribution and Pharmaceutical Practice | 3 | |
| 5. | Organisation and Economics of Pharmaceutical Production | 3 | |
| 6. | Pharmaceutical Technology with Biopharmacy | 3 | |
| 7. | Toxicology and Toxicological Analysis | 3 | |
| 8. | Clinical Chemistry | 3 | |
| V. Specialties for holders of Bachelor degree or Professional Bachelor in “Healthcare Services” degree | |||
| 1. | Anaesthesiology and Intensive Care (for nurses and midwives) | 1 | |
| 2. | Hospital Hygiene (Prevention and Control of Infection) | 1 | |
| 3. | Consultant on Breastfeeding and Healthy and Dietetic Nutrition | 1 | |
| 4. | Nurse for Social Activities | 1 | |
| 5. | Public Healthcare (for nurses, midwives, sanitary inspectors and paramedics) | 1 | |
| 6. | Operating and Dressing Techniques (for nurses and midwives) | 1 | |
| 7. | Psychiatric Care (for nurses and paramedics) | 1 | |
| 8. | Rehabilitation Methods and Treatment of Children with Cerebral Paralysis (for rehabilitation therapists and ergotherapists) | 1 | |
| 9. | Primary Healthcare (for nurses) | 1 | |
| 10. | Emergency Medical Services (for nurses and paramedics) | 1 | |
| 11. | Specific Care of Patients with Oncological Diseases (for nurses and paramedics) | 1 | |
| 12. | Apparatus Maintenance of Extracorporeal Blood Circulation (for nurses and paramedics) | 1 | |
| VI. Specialties for holders of non-medical higher education degree but with Master or Bachelor degree in other field | |||
| 1. | Analysis of Medicinal Products (for chemists) | 3 | |
| 2. | Biochemistry (for biochemists, biologists, molecular biologists and chemists) | 4 | |
| 3. | Biophysics (for biologists and physicists) | 3 | |
| 4. | Virology (for biologists and microbiologists) | 3 | |
| 5. | Healthcare Economics | 2 | |
| 6. | Clinical Psychology (for psychologists) | 3 | |
| 7. | Clinical Chemistry (for chemists, biochemists and biologists) | 3 | |
| 8. | Laboratory Immunology (for biologists, biochemists, molecular biologists, biotechnologists) | 3 | |
| 9. | Medicinal Plants and Herb Uses (for biologists) | 3 | |
| 10. | Medical Zoology (for biologists) | 3 | |
| 11. | Medical Informatics and Health Management | 3 | |
| 12. | Medical Radiological Physics (for physicists and engineers) | 3 | |
| 13. | Medical Sanitary Physics (for engineers and physicists) | 3 | |
| 14. | Medical Gymnastics (for kinesitherapists – methodists in medical gymnastics) | 3 | |
| 15. | Microbiology (for microbiologists and biologists) | 4 | |
| 16. | Radiation Hygiene (for biologists, physicists and chemists) | 3 | |
| 17. | Radiobiology (for biologists, physicists and chemists) | 4 | |
| 18. | Sanitary Chemistry (for chemists) | 3 | |
| 19. | Sanitary Engineering (for engineers and architects) | 3 | |
| 20. | Theoretical Foundations of Medical Chemistry (for chemists) | 3 | |
| 21. | Toxicology (for chemists, biochemists, biologists, molecular biologists, biotechnologists and ecologists) | 3 | |
| 22. | Organisation and Economics of Pharmaceutical Production (for biologists, economists, chemists and chemical engineers) | 3 | |
| VII. Specialties for holders of higher medical degree and non- medical education degree | |||
| 1. | Anatomy, Histology and Cytology (for doctors, doctors of dental medicine, biologists, molecular biologists) | 3 | |
| 2. | Medical Biology (for doctors, biologists, molecular biologists) | 3 | |
| 3. | Medical Pedadgogics (for doctors, doctors of dental medicine, pharmacists, persons with educational and qualification Bachelor degree or Professional Bachelor in “Healthcare Services” degrees, pedagogues and psychologists) | 3 | |
| 4. | Physiology (for doctors, doctors of dental medicine) | 3 | |
| 5. | Legal Regulation in Healthcare (for masters working in the Healthcare system) | 2 | |